Winter is a perfect time to plan! Curl up with your gardening books and the gardening magazines and catalogs you’ve received in the mail. Get out the gardening journal and start dreaming.
General Landscape
- Clean up when you get a break in the weather. Remove fallen branches and downed evergreen clumps. Rake leaves to prevent stains on concrete and dead patches on lawn. If freezing weather is still in the forecast, leave the mulch in place.
- If your Christmas tree is still around, set it where the dropping needles will provide mulch, use the branches as additional insulation for perennials, or get together with neighbors to rent a chipper and create wood chips for larger mulch.
Houseplants
- Perk up tired houseplants by removing dead and dying leaves. Wash under a soft shower in the sink or tub.
- Spider mites love living in warm dry winter homes. Check for mites by looking for tiny speckles on leaves. If so, pick up some Neem Oil or Horticultural Oil or Insecticidal Soap from Bonide.
- Transplant if roots are growing through the drainage holes or over the pot edge. Pick up some new larger trend-setting colored pots to perk up your décor. Or, if you don’t want to move into a larger pot, untangle the roots and cut back by 1/3, scour the pots and replant with new soil.
- Remember to turn your plants each week as they begin to grow towards the weaker window light.
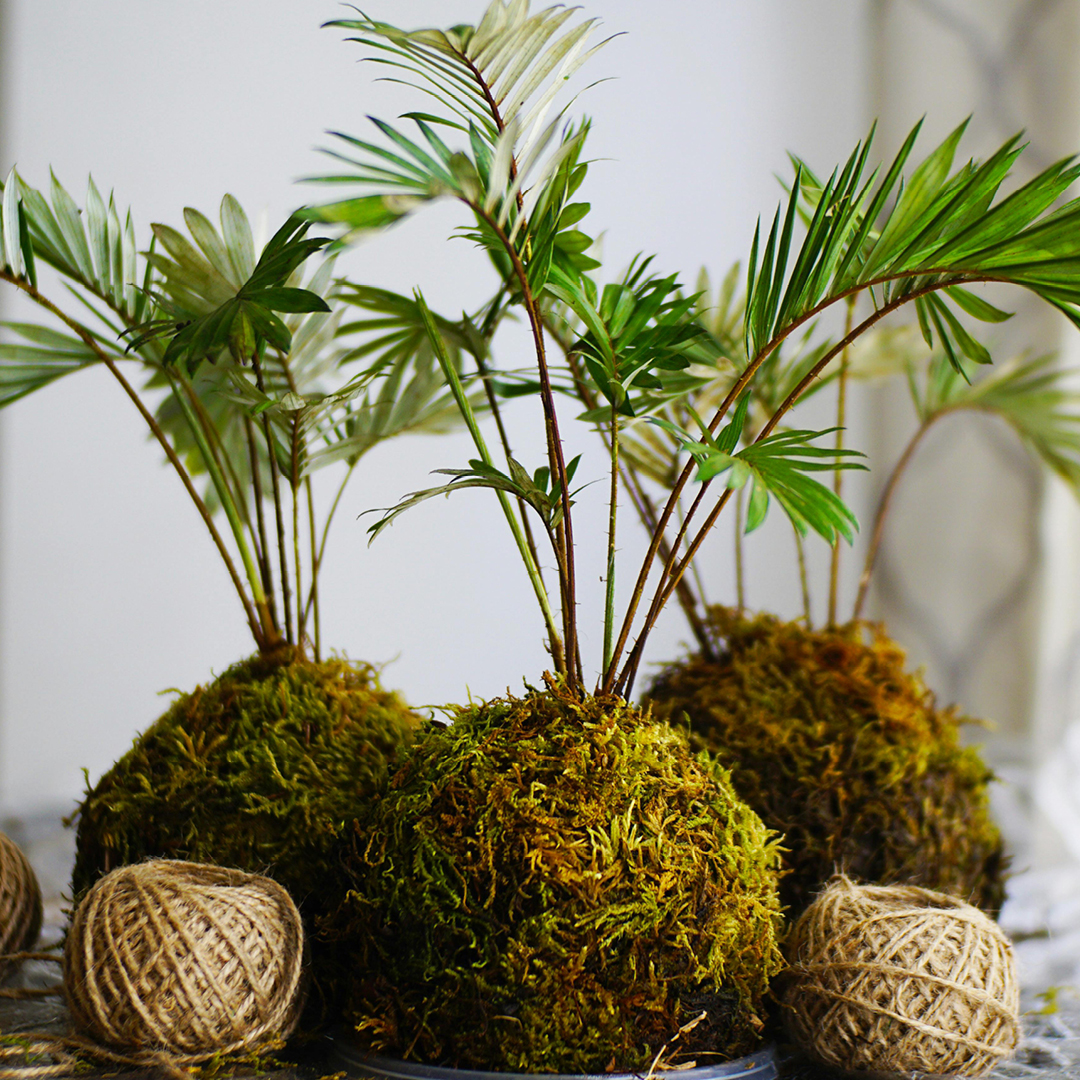
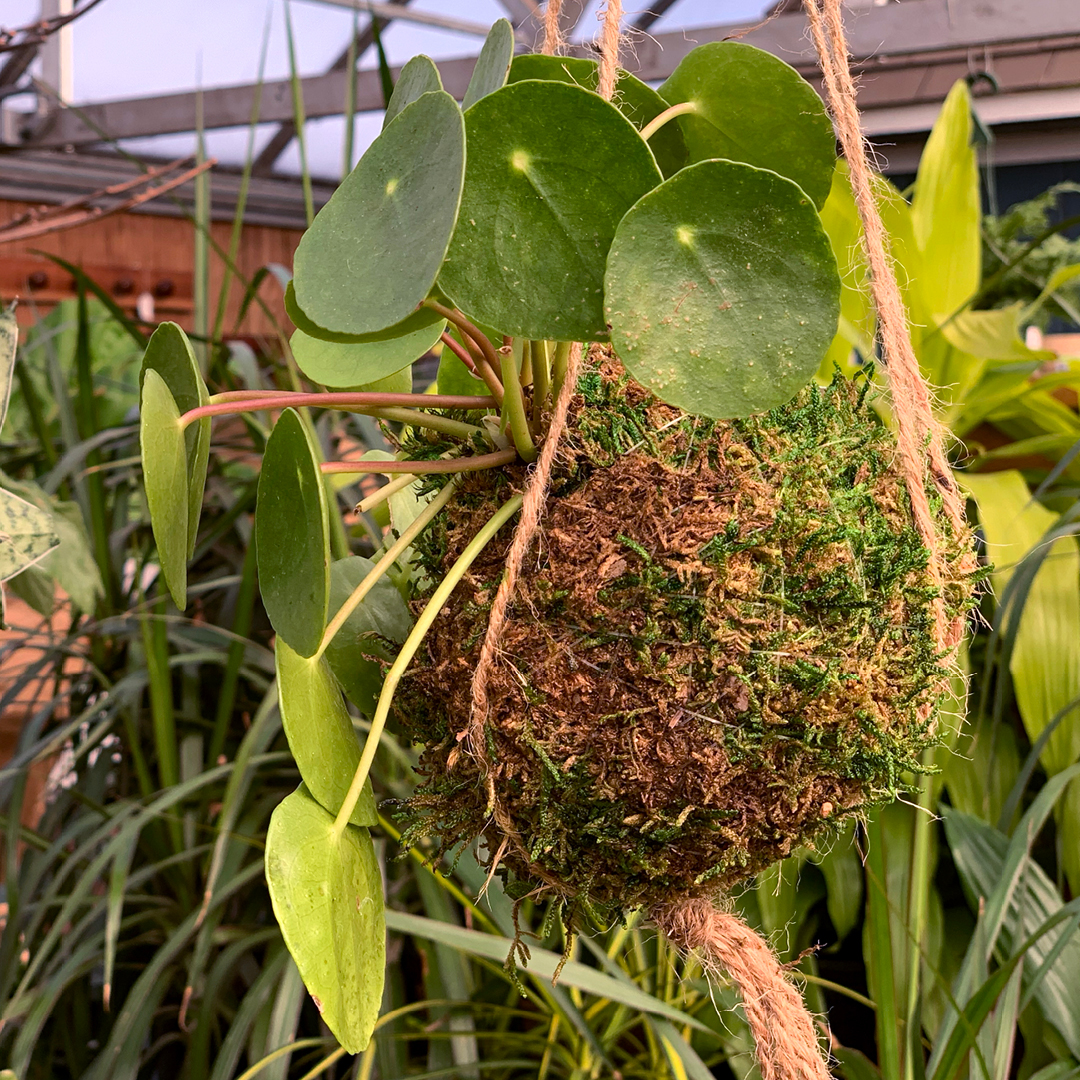
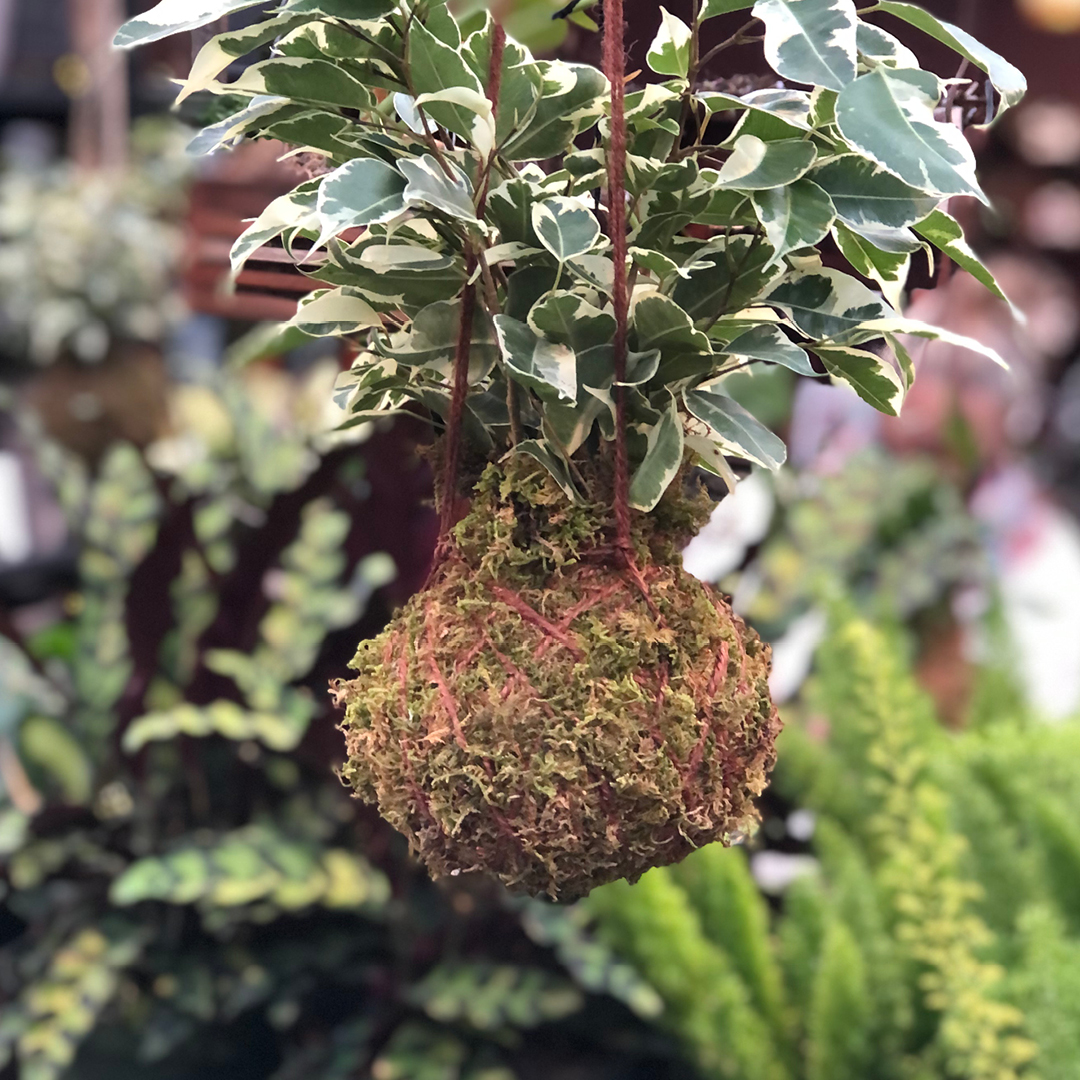
- Plant a terrarium or miniature garden. If you can’t play in the dirt outside, bring the fun indoors!
- Pick up a potted plant for your valentine. Come in and choose from our thriving greenhouse full of succulents, tropicals and houseplants that are the perfect “I love you!”
Vegetables
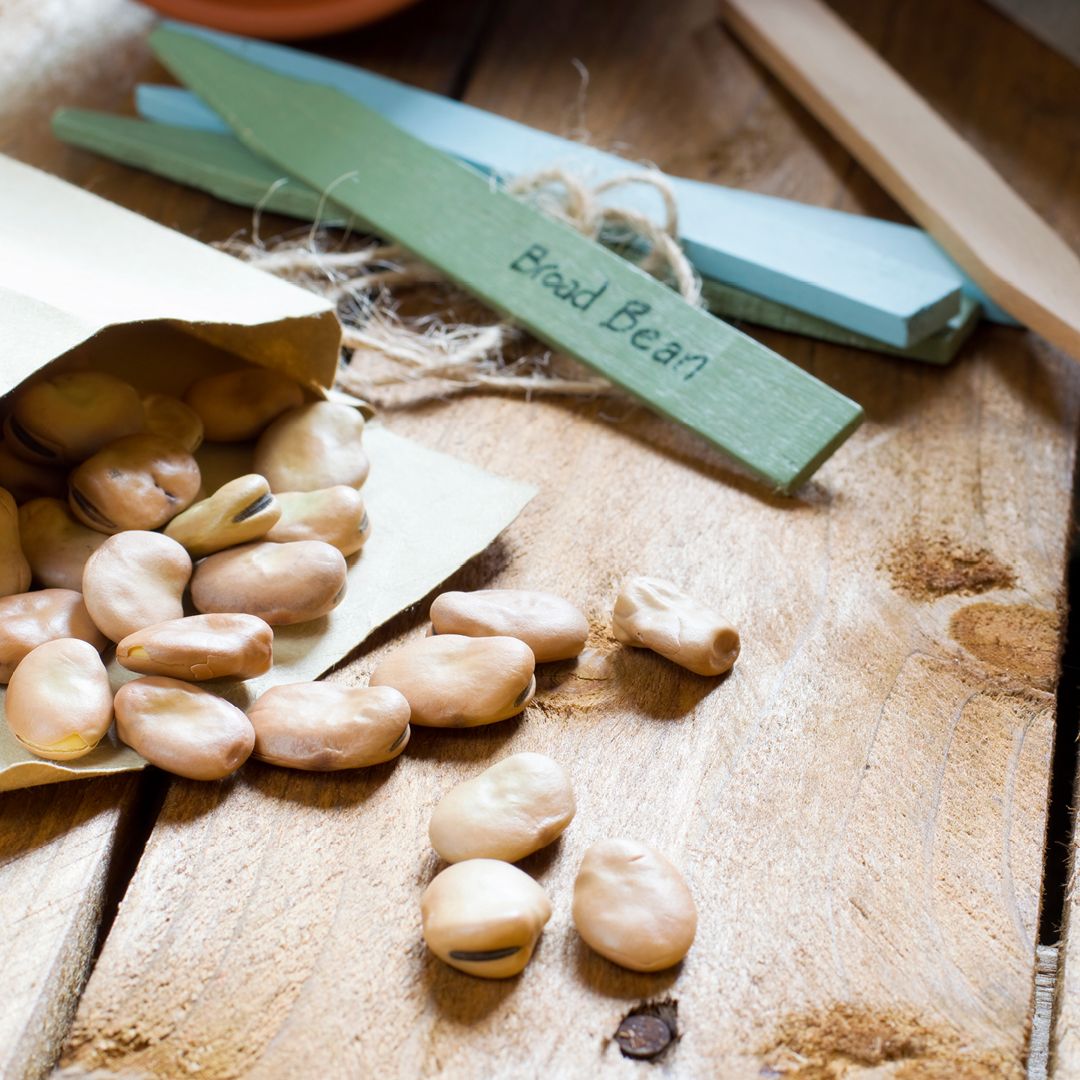
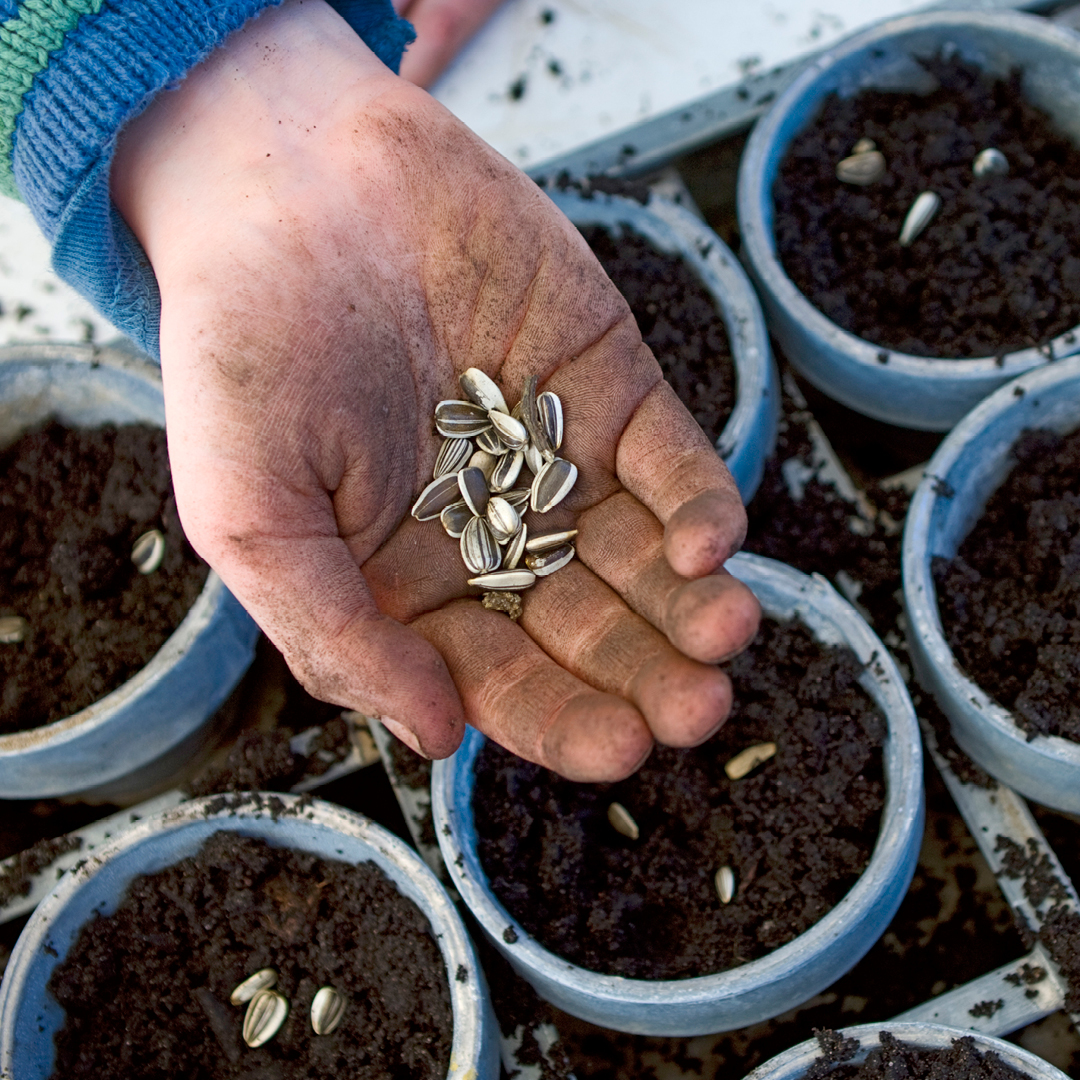
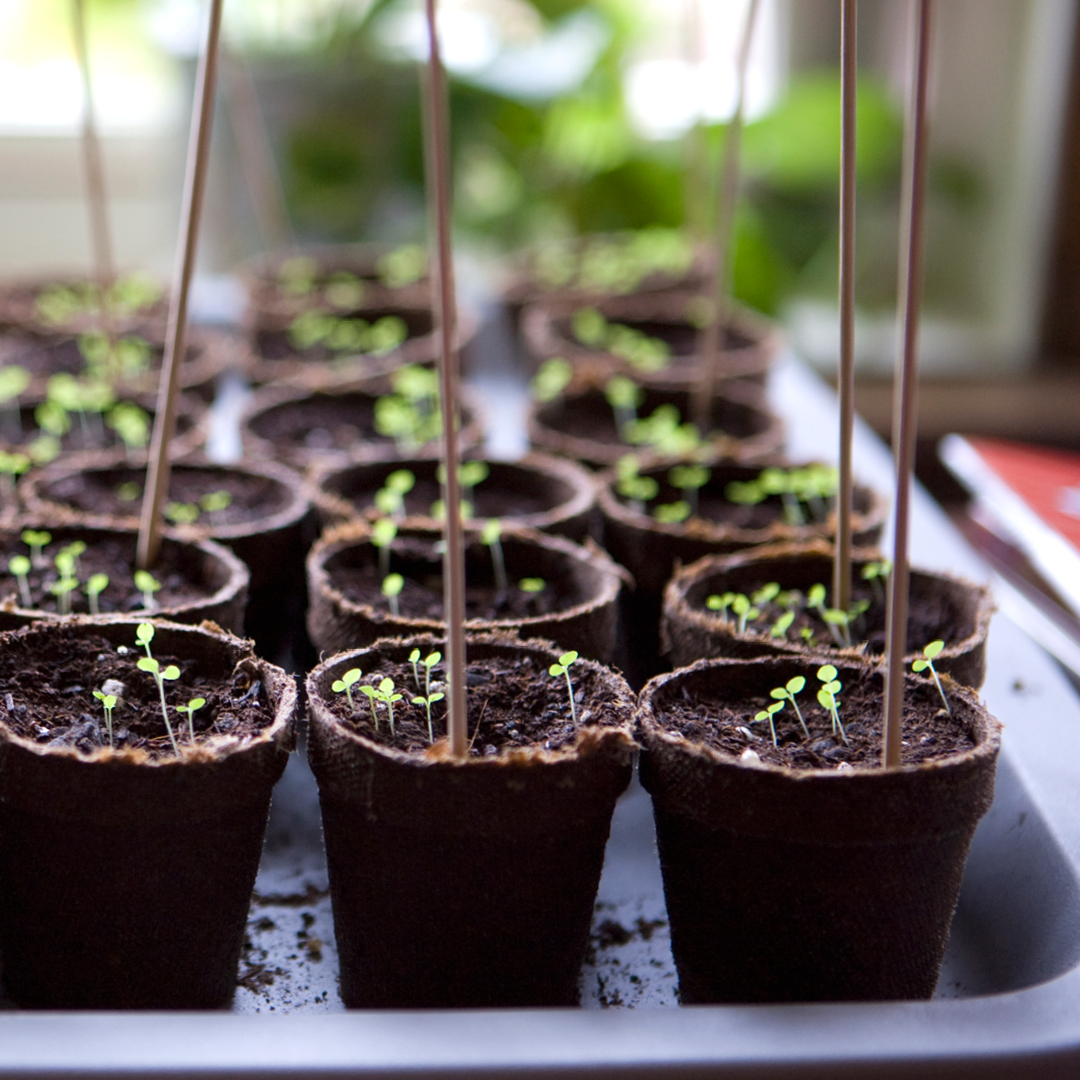
- February: Start vegetable and herb seeds indoors. Pick up some seed trays, heating pads, peat pellets and seed starting mix.
- Sign up for our February 17th class “Seed Starting and Companion Gardening” and learn and companion gardening and different methods for seed starting.
- These veggies need an early start indoors:
| Broccoli Cabbage Celery Chard |
Eggplant Kale Leeks Lettuce |
Scallion Onions, bulb Peppers Tomatoes |
If you just need a breath of aromatic fresh garden air, stop by and smell ours! The humidity is perfect and will instantly transport you to spring. We’d love to see you!